Tattooing involves using a tattoo machine or acupuncture method to pierce dye or ink into the skin according to a designed pattern, forming permanent pigmentation. Some tattoos result from foreign objects entering the skin involuntarily, such as through trauma, leading to permanent skin pigmentation. Due to changes in aesthetics, environment, and social requirements, some individuals seek tattoo removal over time.
Most tattoos are acquired by young men and women who receive professional, amateur, or cosmetic tattoos for beauty or psychological expression. These tattoos use insoluble colored dyes injected into the dermal layer to form pigmentation. Traumatic tattoos occur when foreign bodies enter broken skin after trauma. These foreign bodies can include glass, metal, soil, or carbonaceous materials, with varying depths of skin penetration.
Clinically, tattoos are classified into professional, amateur, cosmetic, traumatic, and other types.
Professional tattoos have clear color boundaries and uniform dyeing with rich colors. Professional tattooists use tattoo equipment to inject one or more organic dyes into the dermal layer at the same depth. The pigments are more stable physically and chemically than those in amateur tattoos. Common colors and their components include mercury for red, cadmium for yellow, chromium for green, and diamond for blue. Red and yellow pigments tend to fade over time.
Amateur tattoos have uneven pigment distribution, indistinct edges, and dull colors, typically gray or blue-black. Non-professionals often use carbon or India ink, with varying injection depths. In China, domestic ink is commonly used, which breaks down more easily than India ink.
Cosmetic tattoos, including lip, eyebrow, and eyeliner tattoos, are common among women. They are often done manually or with tattoo machines, using dyes like brown, black, and red ink, which often contain iron ions or ferric oxide.
Traumatic tattoos show pigmentation from gray to black, caused by the depth of foreign matter entering the skin after trauma. They often occur on exposed parts like the face and hands. Over months or years, some foreign bodies may encapsulate into granulomas in the dermis or subcutaneous tissue, forming palpable induration.
Pathologically, tattoos present as submicron-sized pigment particles of varying shapes and densities in the dermis, often around blood vessels in the superficial and middle dermis layers. Under an electron microscope, tattoos appear as numerous exogenous particles in the dermis, with increased phagocytes engulfing pigment particles.
This condition can generally be diagnosed based on medical history and clinical manifestations.
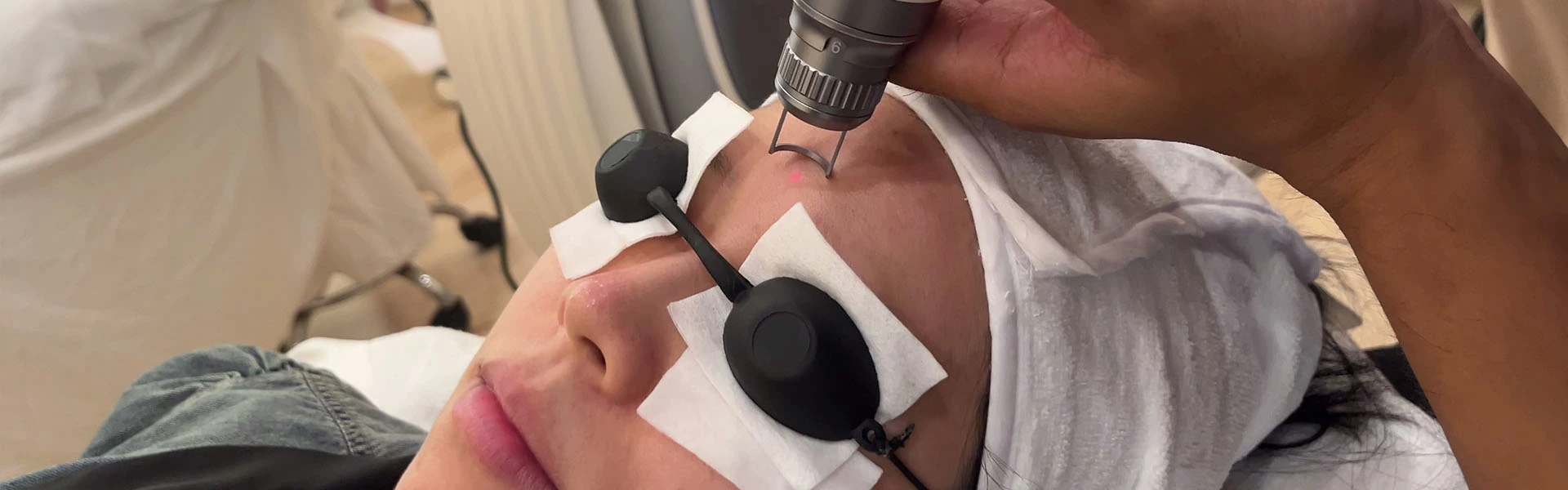
For centuries, various methods have been tried to remove tattoos. Currently, non-laser methods cause more local damage and serious side effects like scars and pigment abnormalities, leading to their gradual elimination.
Q-switched laser is the most effective method for treating undesirable tattoos with minimal adverse reactions. The treatment mechanism is based on the principle of selective photothermal action, where pigment particles absorb laser energy, expand, break into smaller fragments, and are then shed through the body or excreted by phagocytic cells via lymphoid tissue.