Laser treatment is a "double-edged sword". If used well, it can benefit mankind. If used improperly, it can cause permanent damage to the human body. Therefore, strict compliance with quality control requirements and relevant rules and regulations is very important in laser application. significance.
Lasers can be divided into four levels according to their harm to the human body. This is mainly based on the regulations formulated by the U.S. Bureau of Radiation Health.
standard.
Class I laser: Under normal operating conditions, this class of laser poses no radiation hazard to the human body, so control measures are exempted and warning signs are not required. 02 Class II laser: also known as low-power laser. When using it, as long as you operate it carefully, no special safety protection measures are generally required, but warning signs must be used on the outer cover of the machine. Huiwu Class III laser: Also known as medium-power laser, type III-A has a low risk to the human body, and type III-B has a moderate risk to the human body. Since this class of lasers can cause direct harm to the human body, protective measures must be taken. It is strictly forbidden to look directly at the laser beam, and at the same time, laser reflection is reduced as much as possible. Warning signs should be used on the machine's cover.
Class IV laser: This type of laser has high output power and is highly dangerous to the human body. Therefore strict protective measures must be taken and warning signs must be used. It is best to place the same pair of lasers in separate rooms for remote operation.
(1) The laser treatment room must have exhaust equipment.
(2) There should be laser safety warning signs on the door of the laser treatment room.
(3) The laser treatment room should be cleaned or disinfected regularly, and surgical instruments should also be disinfected regularly.
(4) The laser treatment room must have adequate lighting and ventilation conditions, and minimize materials that can form diffuse reflection.
(5) Carbon dioxide laser, erbium laser and other treatments are easy to produce smoke and dust, and the operating room where these equipment are placed must be installed
Dust extraction device.
(6) Medical history information and various items should be managed by dedicated personnel.
(7) Volatile reagents or disinfectants that can be ignited by lasers are prohibited indoors. Huyinyingyan
(3) Safe use of equipment in the treatment room
(1) Only professionally trained personnel are allowed to operate.
(2) The equipment used should have complete product certificates and production licenses, and no products should be used.
(3) The opening, operation, and closing of the equipment must comply with the regulations and requirements of the product manual. Before performing treatment, make sure that all functions of the equipment (especially the cooling function) are operating normally.
(4) Laser equipment should be managed by dedicated personnel, and the laser beam should not be irradiated on metal surfaces.
(5) The equipment should be maintained and maintained regularly, and parameters such as power should be tested regularly.
(6) The power supply must be inspected and maintained regularly.
(4) Requirements for operators
(1) Laser medical technicians must have relevant professional qualifications.
(2) Physicians engaged in skin laser treatment should have certain clinical experience in dermatology.
(3) Physicians engaged in skin laser treatment should undergo formal training and master the basic knowledge of laser, laser technical parameters and operating methods.
(4) Practitioners should receive regular training and re-education.
(5) Operating procedures
(1) Have a preoperative conversation with the patient and their family members to inform them of the possible risks and postoperative precautions of laser surgery, so that the patient's expectations can reach a reasonable level. All patients should sign an informed consent form before surgery.
(2) Carry out preoperative preparations as usual, clean and disinfect the surgical area as needed, and perform local disinfection if necessary.
Local anesthesia and topical anesthesia. The use of anesthetics should follow safe and standardized principles.
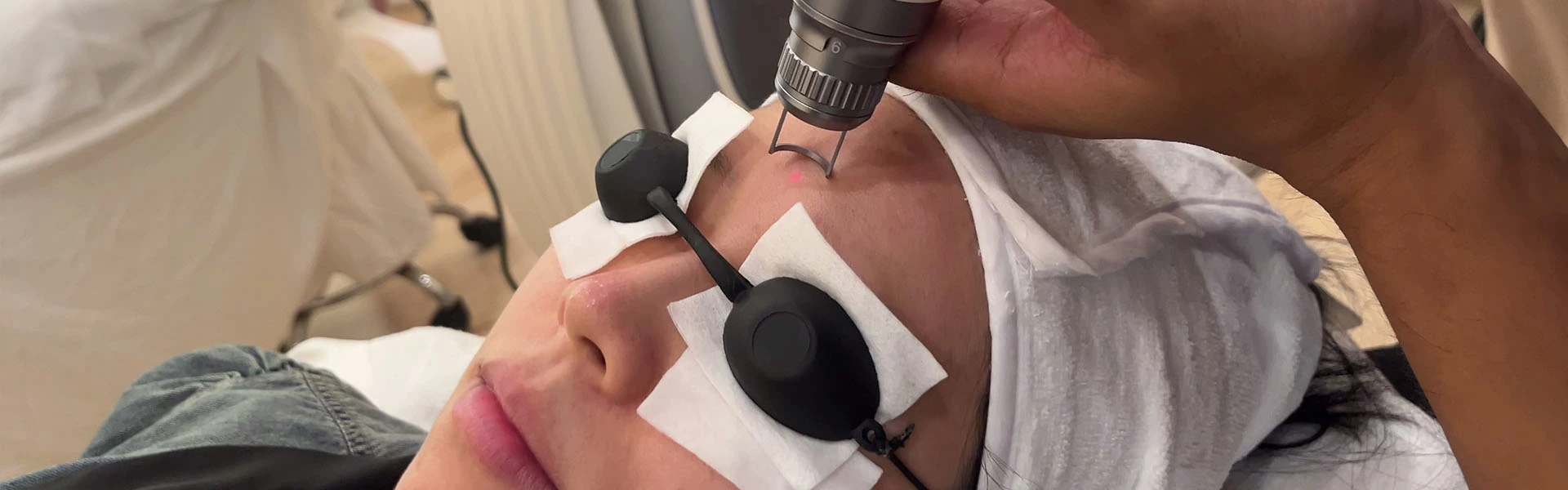
(3) Based on the diagnosis of the patient, select the appropriate laser and laser parameters for treatment. During treatment, the surrounding normal skin must be properly protected, and staff should wear protective goggles to protect their eyes.
(4) After treatment, apply a protective agent externally to the wound as needed to prevent infection.
(5) Postoperative infection should be avoided, external or oral antibiotics can be used, and scratching and strenuous exercise should be avoided in the treatment area.
Sun exposure should be avoided after cosmetic laser or photorejuvenation surgery.
(6) If the patient has any unexpected situation after surgery, he should contact the doctor as soon as possible and follow up for follow-up consultation.
(6) Personnel safety protection
(1) Class II~IV lasers should be labeled with warning signs.
(2) During treatment, unrelated persons should be prevented from entering or staying at the site.
(3) There should be sufficient lighting during laser treatment to shrink the pupils and protect the eyes; at the same time, direct gaze is strictly prohibited
Laser beam. (4) During treatment, staff should wear special protective goggles according to the wavelength of the treatment laser; patients should cover their eyes with black goggles or soaked gauze.
(5) During treatment, attention should be paid to protecting the normal skin outside the treatment area; the operator should wear long-sleeved overalls, and the laser head should be aimed at the treatment area during operation, and should not be turned in any direction.
(6) Strengthen education on laser safety and protection.