The Basics of Acne - Causes and Triggers

The Basics of Acne - Causes and Triggers
The Basics of Acne: Causes and Triggers
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide, transcending age, gender, and ethnicity. Understanding its causes and triggers can help manage and prevent outbreaks, leading to clearer and healthier skin.
What is Acne?
Acne is a skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. While it is most prevalent among teenagers, it can affect individuals during all stages of life. Acne can manifest as whiteheads, blackheads, pimples, cysts, or nodules, primarily appearing on the face, forehead, chest, upper back, and shoulders.
Primary Causes of Acne
-
Excessive Oil Production: The sebaceous glands in our skin produce an oily substance known as sebum. When these glands produce excess oil, it can clog pores.
-
Hair Follicles Clogged by Dead Skin Cells: Dead skin cells can accumulate in hair follicles, creating a plug that prevents oil from reaching the skin's surface.
-
Bacteria: The bacteria Propionibacterium acnes, which naturally resides on the skin, can proliferate in blocked follicles, leading to inflammation and pimples.
-
Hormonal Changes: Hormones, especially androgens, can increase the size of sebaceous glands and oil production. This is why acne is often associated with puberty, menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and certain medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Common Triggers of Acne
-
Diet: Certain foods, particularly those with a high glycemic index like refined sugars and carbohydrates, have been linked to acne flare-ups.
-
Stress: Stress stimulates the production of hormones like cortisol, which can exacerbate acne.
-
Medications: Drugs such as corticosteroids, lithium, and certain anticonvulsants can trigger or worsen acne.
-
Cosmetic Products: Some skincare and hair care products can clog pores and provoke acne, commonly known as acne cosmetica.
-
Environmental Factors: Pollution, humidity, and prolonged exposure to sun or sweat can worsen acne conditions.
Managing Acne
Managing acne involves a comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle changes, skincare routines, and sometimes medical treatments.
-
Skincare Routine: Gentle cleansing twice a day, using non-comedogenic products, and avoiding irritants are fundamental steps. Exfoliation can help remove dead skin cells but should be done sparingly to prevent irritation.
-
Dietary Adjustments: Reducing the intake of high glycemic foods and incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can be beneficial.
-
Stress Management: Practices like yoga, meditation, and adequate sleep are crucial in managing stress levels.
-
Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter products containing benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or alpha hydroxy acids can help reduce inflammation and unclog pores.
-
Prescription Treatments: In more severe cases, dermatologists may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics, retinoids, or hormonal therapy.
The Role of Skin Whitening Treatments
Though acne is primarily associated with oil production and bacteria, uneven skin tone and hyperpigmentation resulting from acne scars can be significant concerns. Consequently, skin whitening treatments are often sought to address these issues.
Underarm Skin Whitening Treatment and other skin whitening treatments often promise to reduce hyperpigmentation and promote an even skin tone. These treatments may contain ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, or vitamin C, which inhibit melanin production and lighten the skin.
While these treatments can improve the appearance of acne scars and hyperpigmentation, it is essential to use them under the guidance of a dermatologist to avoid potential side effects and ensure they are appropriate for your skin type.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes and triggers of acne is the first step in effectively managing and preventing it. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, adhering to a suitable skincare routine, and seeking professional treatment when necessary, individuals can achieve clearer, healthier skin. Moreover, addressing post-acne hyperpigmentation with appropriate skin whitening treatments can further enhance skin appearance, providing a holistic approach to skincare.
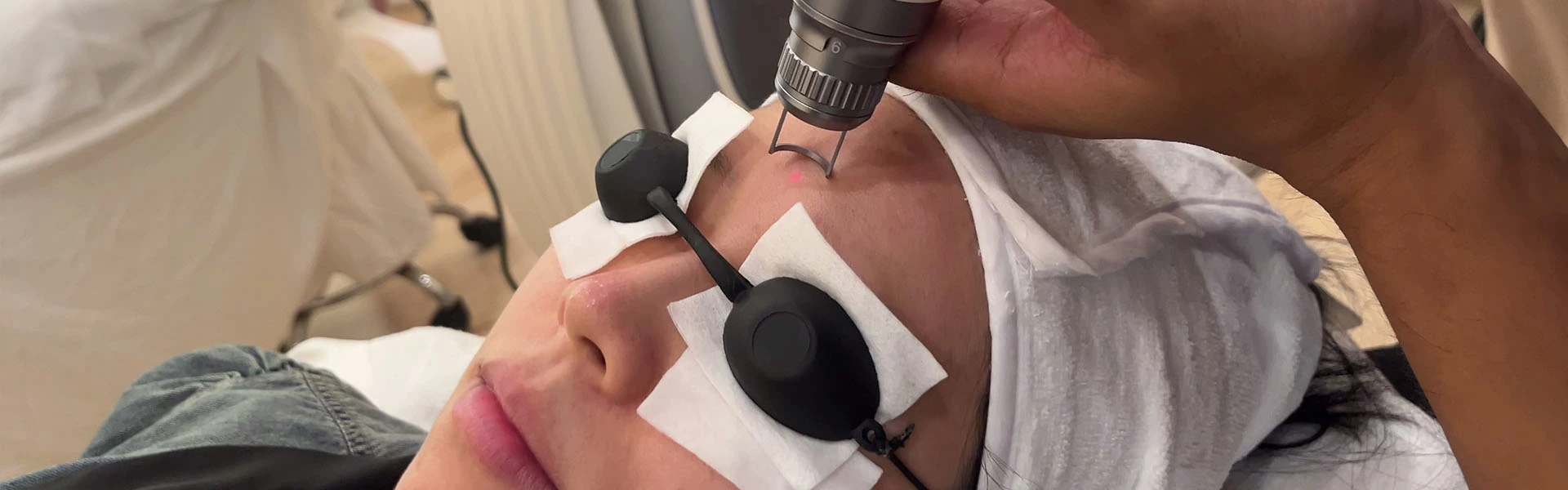
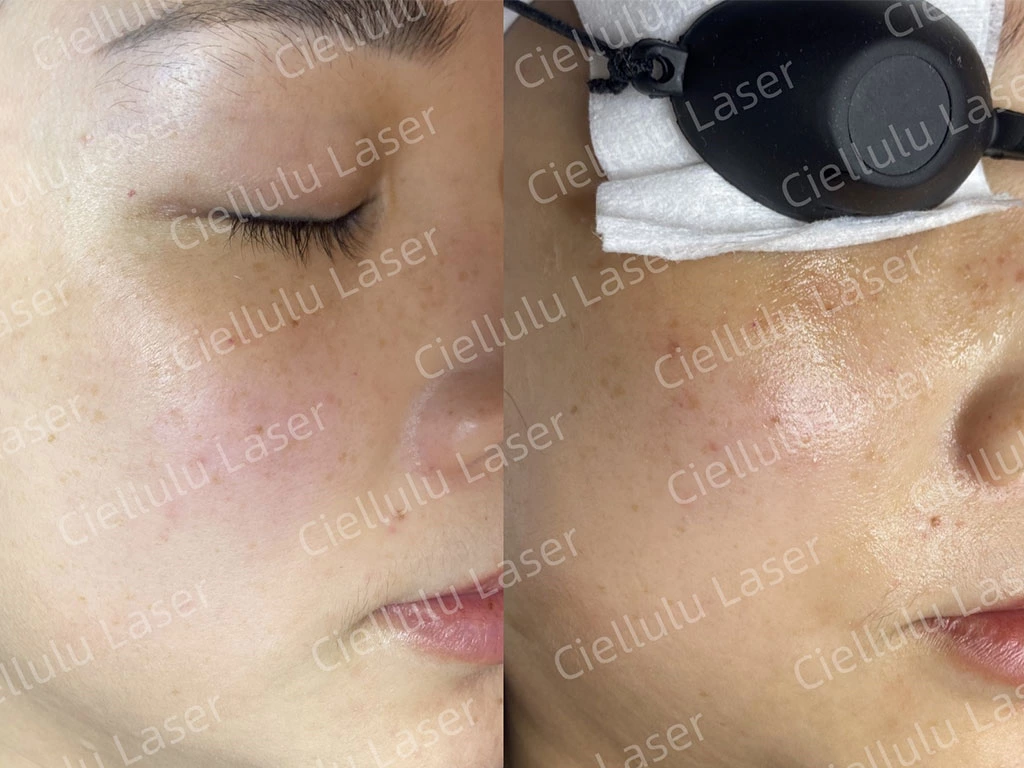

 Ciellulu Laser - Facial Machine Supplier
Ciellulu Laser - Facial Machine Supplier

